FerrazziJosephBSUGEOG
Thursday, April 13, 2017
Wednesday, April 12, 2017
lab 8
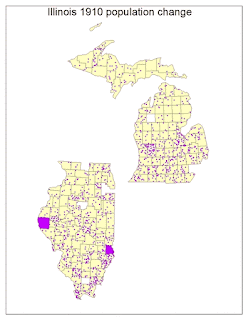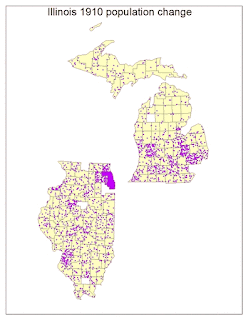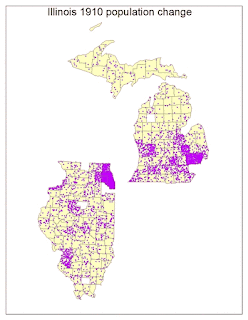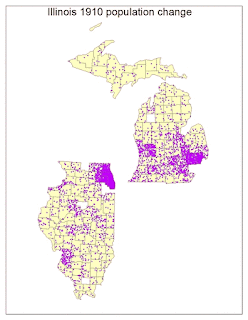
I ran into multiple obstacles in Lab 8. When learning to classify my population change data from the previous lab, there were missing spots coming up in my data. After multiple tries of trying to fix these missing spots, we decided to move along with the data including these missing spots. We found out these missing spots ended up being from counties that were not included in the ARCGIS counties files versus my own data that I looked up. It seems as though over the years, the counties were put together into one for many circumstances. I decided to pick five classes. The classification scheme that worked best for most of my data was natural breaks. Natural breaks separate according to logical break points and considers the distribution of the data. It also clearly shows the clusters and outliers in my data. This was also the final classification theme I went with due to it being easy to compare to other maps. I modified this scheme and changed the break values and made it my own so that it would work for all of my maps.
A color ramp provides the means to apply a range of colors to a group of symbols. I decided to go with an Algorithmic color ramp. These color ramps are a linear stretch between two specified colors designed to convey the amount or degree of a quantitative distribution. Mine goes from yellow to red. For both my graduated and proportional symbol maps, I decided to use a circle as my shape. I decided to use a circle because it is a compact symbol, and its smooth visual impression is good for my type of data. For my graduated symbol map I decided to use different hues of blue, and the proportional symbol map I used different hues of green. Using a single-ended hue worked well with the type of data I was showing. For dot density, I also chose one color that worked well to display my data the best.
Wednesday, March 22, 2017
Lab 7
 NAD 1983 contiguous USA Albers
XLS FILE- An XSL style sheet is, like with CSS, a file that describes how to display an XML document of a given type. XSL shares the functionality and is compatible with CSS2
Select by Attributes-Select By Attributes allows you to provide a SQL query expression that is used to select features that match the selection criteria
Query-A request to select features or records from a database. A query is often written as a statement or logical expression.
Fields-Tables form the foundation of geographic data and are the fundamental building blocks of any data model. Tables are a collection of information, such as a list of building owners, employees, or customer information. Layers in a map, such as city streets, buildings, or address points, are simply tables that include information about the geometry and location of those features.
Records-
Attributes-There are two components to GIS data: spatial information (coordinate and projection information for spatial features) and attribute data. Attribute data is information appended in tabular format to spatial features
Relational Database-A data structure in which collections of tables are logically associated with each other by shared fields.
Join Function-Joining data is typically used to append the fields of one table to those of another through an attribute or field common to both tables. You can choose to define the join based on either attributes or a predefined geodatabase relationship class or by location (also referred to as a spatial join). You will only see join by relationship class listed if you are joining geodatabase data for which a relationship class has already been defined in the geodatabase.
Calculate/ Field Calculator-In some cases, you might want to perform a mathematical calculation to set a field value for a single record or even all records. You can perform simple as well as advanced calculations on all or selected records. In addition, you can calculate area, length, perimeter, and other geometric properties on fields in attribute tables
NAD 1983 contiguous USA Albers- The Albers equal area conic is the typical projection for historical USGS maps of the lower 48, it being a general-purpose low-distortion compromise for mid-latitude short and wide extents.
NAD 1983 contiguous USA Albers
XLS FILE- An XSL style sheet is, like with CSS, a file that describes how to display an XML document of a given type. XSL shares the functionality and is compatible with CSS2
Select by Attributes-Select By Attributes allows you to provide a SQL query expression that is used to select features that match the selection criteria
Query-A request to select features or records from a database. A query is often written as a statement or logical expression.
Fields-Tables form the foundation of geographic data and are the fundamental building blocks of any data model. Tables are a collection of information, such as a list of building owners, employees, or customer information. Layers in a map, such as city streets, buildings, or address points, are simply tables that include information about the geometry and location of those features.
Records-
Attributes-There are two components to GIS data: spatial information (coordinate and projection information for spatial features) and attribute data. Attribute data is information appended in tabular format to spatial features
Relational Database-A data structure in which collections of tables are logically associated with each other by shared fields.
Join Function-Joining data is typically used to append the fields of one table to those of another through an attribute or field common to both tables. You can choose to define the join based on either attributes or a predefined geodatabase relationship class or by location (also referred to as a spatial join). You will only see join by relationship class listed if you are joining geodatabase data for which a relationship class has already been defined in the geodatabase.
Calculate/ Field Calculator-In some cases, you might want to perform a mathematical calculation to set a field value for a single record or even all records. You can perform simple as well as advanced calculations on all or selected records. In addition, you can calculate area, length, perimeter, and other geometric properties on fields in attribute tables
NAD 1983 contiguous USA Albers- The Albers equal area conic is the typical projection for historical USGS maps of the lower 48, it being a general-purpose low-distortion compromise for mid-latitude short and wide extents.
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)